LATEST RELEASE BY MVTec
MERLIC 5.7 & HALCON 24.11
The new MERLIC 5.7 version improves the usability of MERLIC Runtime Environment (RTE) and optimizes the handling of communication interfaces.
HALCON 24.11 introduces groundbreaking features like Deep 3D Matching, enabling robust and precise object detection for bin-picking and pick-and-place applications using synthetic CAD data — no additional training required. Plus, experience the preview of HDevelopEVO, a modern IDE with an intuitive interface and enhanced programming efficiency.

Newest features of
MERLIC 5.7
On April 3, 2025, MVTec launched MERLIC 5.7. The new version improves the usability of MERLIC Runtime Environment (RTE) and optimizes the handling of communication interfaces.
MVTec MERLIC includes both powerful conventional and state-of-the-art deep learning methods. In addition, its graphical user interface enables users to intuitively create complete machine vision applications.

Watch the MERLIC 5.7 webinar now!
Would you like to watch the new MERLIC 5.7 webinar and learn more about our latest features? Then register and have fun streaming!
Please note: If you do not see a registration form, please disable your ad blocker.

What's changing?
MERLIC 5.7 optimizes integration into the machine control system by managing communication plug-ins directly in the MERLIC Runtime Environment (RTE). This reduces components, improves usability and simplifies deployment. In addition, the MERLIC frontend is now available for Linux and can be used as a remote frontend, enabling flexible system architectures. New sample Dockerfiles and scripts facilitate containerized deployment and integration into existing workflows.
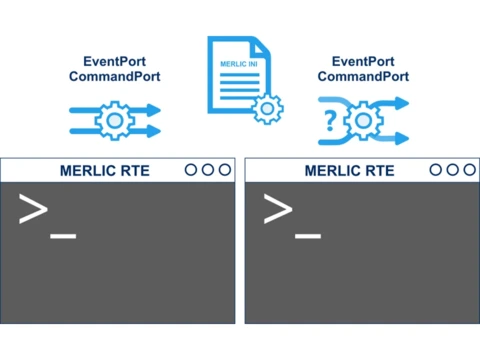
Simplified integration of MERLIC into machine control
In MERLIC 5.7, the process of integrating MERLIC into machine control has been further streamlined. Configuring and running communication plug-ins now only requires MERLIC Runtime Environment (RTE), eliminating the need to start and manage an additional process, as was necessary in previous versions. By integrating plug-in management into RTE, the number of required components has been reduced, usability improved, and deployment further simplified. For example, it is now possible to run two MERLIC RTE instances in parallel without manually configuring ports. Additionally, plug-in messages are now logged directly in the MERLIC RTE log file, which significantly simplifies debugging.
Example Dockerfiles and scripts for containerized deployment
The simple deployment of machine vision applications across different environments is becoming increasingly important.
Starting with version 5.7, MERLIC includes example Dockerfiles and scripts for creating custom containers. This simplifies the setup process and enables seamless integration of both MERLIC Frontend and MERLIC RTE into existing containerized workflows. This enhances flexibility in deploying and managing MERLIC.

Major features of
HALCON 24.11
In this release, users benefit from groundbreaking technologies and improvements. With HALCON 24.11, we are focusing on even better AI, specifically deep learning algorithms. Among other features, users can now detect and evaluate unexpected behavior in deep-learning-based classification.
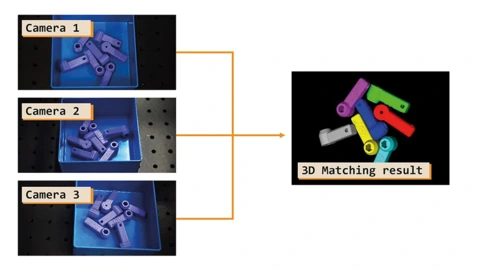
Deep 3D Matching
With this feature, HALCON 24.11 contains a deep-learning-based market innovation for the 3D vision sector, especially for bin-picking and pick-and-place applications.
This feature is particularly robust in determining the exact position and rotation of a trained object, and is characterized by very low parameterization effort and fast execution time. Depending on the accuracy requirements, one or more cost-efficient standard 2D cameras can be used to determine the position. Training is performed exclusively on synthetic data generated from a CAD model. Further training is therefore not required.
Customers can already run this feature in HALCON 24.11 – to train the model and evaluate applications, they can contact MVTec at any time. Training and evaluation within HALCON will follow in the next release.
Out of Distribution Detection (OOD) for Classification
This new HALCON feature makes it easy to recognize unexpected behavior caused by incorrect classifications in production. Thus, users can take appropriate measures, such as stopping the machine, in a targeted and efficient manner. When using a deep learning classifier, unknown objects are assigned to one of the classes that the system has learned. This can lead to problems if, for example, the defects or objects themselves are of a type that has never occurred before. The new deep learning feature “Out of Distribution Detection (OOD)” indicates when an object is classified that was not included in the training data. For example, this could be a bottle with a green label if the system was only trained on bottles with red or yellow labels. In such cases, HALCON provides the message “Out of Distribution” together with an OOD score that indicates how much the deviation from the trained classes is.
The OOD score can also be useful when expanding deep learning models with new training images by indicating which of the new images will have the greatest value for the new model. For example, a high OOD score for a new training image indicates a greater deviation from the images already in the network – this means a higher information content and, therefore, greater value for the training.

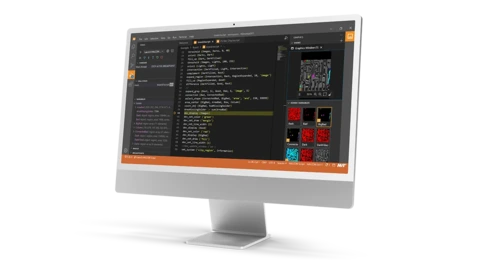
Preview of the new IDE HDevelopEVO
HALCON 24.11 has a special highlight for all users of HALCON’s own integrated development environment (IDE) HDevelop: a preview of the new IDE HDevelopEVO. This is characterized, among other things, by a more modern, intuitive user interface and an improved editor (i.e., the central programming element). The latter enables faster and more efficient programming and prototyping of machine vision applications. Users can already extensively test the new development environment in HALCON 24.11. The range of functions of HDevelopEVO will be continuously expanded in the coming releases and it will over time become the standard HALCON development environment.
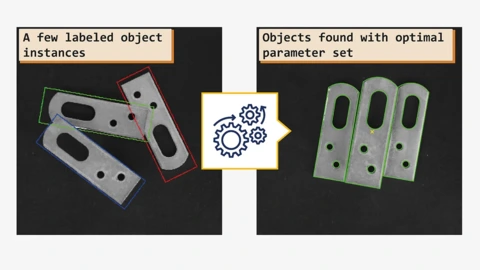
Improved Shape-based Matching
The new HALCON version makes the “Shape-based Matching” feature, used in many applications, more user-friendly.
This technology is used to find objects fast, accurately, and precisely. HALCON 24.11 includes the new patent pending “Extended Parameter Estimation” for this purpose. This allows parameters to be estimated with greater granularity, which significantly speeds up execution in some applications. “Extended Parameter Estimation” enables this estimation also for users without in-depth machine vision expertise.

Optimized QR code reader
The performance of HALCON’s QR Code Reader has been significantly increased.
This is particularly evident under difficult conditions, for example, when many codes need to be found in the image area or many textures in the image complicate the detection. The recognition rate has been increased and the evaluation time has been significantly reduced in demanding scenarios.
HALCON’s GigE Vision interface supports RoCEv2
With this release, HALCON’s GigE Vision interface supports the RoCEv2 network protocol, which enables increased performance in image transmission.
Improved HALCON Progress edition
HALCON Progress is now fully compatible with the HALCON Steady edition. Progress users can now collaborate with Steady users on the same projects. Additionally, HALCON Progress users will receive the same maintenance updates as HALCON Steady users. In the future, switching from Steady to Progress will simply require exchanging the license file.
Watch the recorded HALCON 24.11 webinar
Would you like to watch the new HALCON 24.11 webinar and learn more about our latest features? Then register and have fun streaming!
Please note: If you do not see a registration form, please disable your ad blocker.
